A wheel provided with suitably shaped teeth, receiving an intermittent circular motion from an oscillating or reciprocating member, is called a ratchet wheel. A simple form of ratchet mechanism is shown in Figure 12-1.
A is the ratchet wheel, and B is an oscillating lever carrying the driving pawl, C. A supplementary(辅助的) pawl at D prevents backward motion of the wheel.
When arm B moves counterclockwise, pawl C will force the wheel through a fractional part of a revolution dependent upon the motion of B. When the arm moves back (clockwise), pawl C will slide over the points of the teeth while the wheel remains at rest because of fixed pawl D, and will be ready to push the wheel on its forward (counterclockwise) motion as before.
The amount of backward motion possible varies with the pitch of the teeth. This motion could be reduced by using small teeth, and the expedient(权益之计) is sometimes used by placing several pawls side by side on the same axis, the pawls being of different lengths.
 The contact surfaces of wheel and pawl should be inclined so that they will not tend to disengage(脱离) under pressure. This means that the common normal(公法线) at N should pass between the pawl and the ratchet-wheel centers. If this common normal should pass outside these limits, the pawl would be forced out of contact under load unless held by friction. In many ratchet mechanisms the pawl is held against the wheel during motion by the action of a spring.
The contact surfaces of wheel and pawl should be inclined so that they will not tend to disengage(脱离) under pressure. This means that the common normal(公法线) at N should pass between the pawl and the ratchet-wheel centers. If this common normal should pass outside these limits, the pawl would be forced out of contact under load unless held by friction. In many ratchet mechanisms the pawl is held against the wheel during motion by the action of a spring.
The usual form of the teeth of a ratchet wheel is that shown in Figure 11-2, but in feed mechanisms such as used on many machine tools it is necessary to modify the tooth shape for a reversible pawl so that the drive can be in either direction.
If you try this mechanism, you may turn the crank of the link mechanism. The rocker will drive the driving pawl to drive the ratchet wheel.
2 Overrunning Clutch(超越离合器)
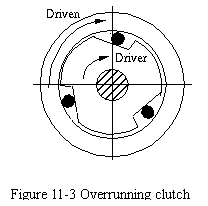 A special form of a ratchet is the overrunning clutch. Have you ever thought about what kind of mechanism drives the rear axle of bicycle? It is a free-wheel mechanism which is an overrunning clutch. Figure 11-3 illustrates a simplified model. As the driver delivers torque to the driven member, the rollers or balls are wedged into the tapered recesses. This is what gives the positive drive. Should the driven member attempt to drive the driver in the directions shown, the rollers or balls become free and no torque is transmitted.
A special form of a ratchet is the overrunning clutch. Have you ever thought about what kind of mechanism drives the rear axle of bicycle? It is a free-wheel mechanism which is an overrunning clutch. Figure 11-3 illustrates a simplified model. As the driver delivers torque to the driven member, the rollers or balls are wedged into the tapered recesses. This is what gives the positive drive. Should the driven member attempt to drive the driver in the directions shown, the rollers or balls become free and no torque is transmitted.
3 Intermittent Gearing(简歇运动机构)
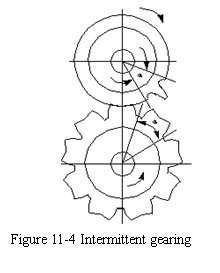 A pair of rotating members may be designed so that, for continuous rotation of the driver, the follower will alternately roll with the driver and remain stationary. This type of arrangement is known by the general term intermittent gearing. This type of gearing(传动) occurs in some counting mechanisms(计数机构), motion-picture machines(电影放映机) , feed mechanisms, as well as others.
A pair of rotating members may be designed so that, for continuous rotation of the driver, the follower will alternately roll with the driver and remain stationary. This type of arrangement is known by the general term intermittent gearing. This type of gearing(传动) occurs in some counting mechanisms(计数机构), motion-picture machines(电影放映机) , feed mechanisms, as well as others.
The simplest form of intermittent gearing, as illustrated in Figure 11-4 has the same kind of teeth as ordinary gears designed for continuous rotation. This example is a pair of 18-tooth gears modified to meet the requirement that the follower advance one-ninth of a turn for each turn of the driver. The interval(间隔) of action is the two-pitch angle (indicated on both gears). The single tooth on the driver engages with each space on the follower to produce the required motion of a one-ninth turn of the follower. During the remainder of a driver turn, the follower is locked against rotation in the manner shown in the figure 11-4.
To vary the relative movements of the driver and follower, the meshing teeth can be arranged in various ways to suit requirements. For example, the driver may have more than one tooth, and the periods of rest of the follower may be uniform or may vary considerably. Counting mechanisms are often equipped with gearing of this type.
4 The Geneva Wheel(槽轮机构)
An interesting example of intermittent gearing is the Geneva Wheel shown in Figure 11-5. In this case the driven wheel, B, makes one fourth of a turn for one turn of the driver, A, the pin, a, working in the slots, b, causing the motion of B. The circular portion of the driver, coming in contact with the corresponding hollow circular parts of the driven wheel, retains it in position when the pin or tooth a is out of action. The wheel A is cut away near the pin a as shown, to provide clearance(间隙) for wheel B in its motion.
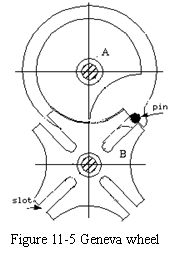 If one of the slots is closed, A can only move through part of the revolution in either direction before pin a strikes the closed slot and thus stops the motion. The device in this modified form was used in watches, music boxes, etc., to prevent overwinding(过卷绕). From this application it received the name Geneva stop. Arranged as a stop, wheel A is secured to the spring shaft, and B turns on the axis of the spring barrel(发条匣). The number of slots or interval units in B depends upon the desired number of turns for the spring shaft.
If one of the slots is closed, A can only move through part of the revolution in either direction before pin a strikes the closed slot and thus stops the motion. The device in this modified form was used in watches, music boxes, etc., to prevent overwinding(过卷绕). From this application it received the name Geneva stop. Arranged as a stop, wheel A is secured to the spring shaft, and B turns on the axis of the spring barrel(发条匣). The number of slots or interval units in B depends upon the desired number of turns for the spring shaft.

5 The Universal Joint s(万向联轴节)
The engine of an automobile is usually located in front part. How does it connect to the rear axle of the automobile? In this case, universal joints are used to transmit the motion.
 The universal joint as shown in Figure 13-6 is also known in the older literature as Hooke''s coupling. Regardless of how it is constructed or proportioned, for practical use it has essentially the form shown in Figure 13-7, consisting of two semicircular forks 2 and 4, pin-jointed to a right -angle cross 3.
The universal joint as shown in Figure 13-6 is also known in the older literature as Hooke''s coupling. Regardless of how it is constructed or proportioned, for practical use it has essentially the form shown in Figure 13-7, consisting of two semicircular forks 2 and 4, pin-jointed to a right -angle cross 3.
The driver 2 and the follower 4 make the complete revolution at the same time, but the velocity ratio is not constant throughout the revolution(转).
Vocabulary
1.intermittent adj.间歇的
2.oscillating n.摆动的
3.reciprocating adj. 往复的,交替的
4.ratchet wheel 棘轮
5.driving pawl 棘爪
6.supplementary adj. 辅助的
7.counterclockwise adj. 逆时针的
8.fractional adj. 部分的
9.pitch n. 间距
10.expedient n. 权益之计; adj. 有利的
11.inclined adj. 倾斜的
12.disengage v. 脱离
13.common normal 共法线
14.Overrunning Clutch 超越离合器
15.axle n. 车轴;轮轴
16.free-wheel 飞轮;滑轮
17.illustrate vt. 图解;举例说明
18.wedge into v. 楔入
19.recess n. 凹穴;槽
20.deliver v. 运、送;提供;输送
21.intermittent a. 间歇的
22.ordinary a. 普通的;正常的
23.The Geneva Wheel 槽轮机构
24.clearance n. 间隙
25.overwind v 过渡卷绕;旋得太紧
26.secure v. 紧闭;固定
27.barrel N. 圆柱体
28.The Universal Joint 万向联轴节
29.literature N. 文献
30.Hooke''s coupling 万向联轴节
31.proportion v. 成比例;配合
1;所有标注为智造资料网zl.fbzzw.cn的内容均为本站所有,版权均属本站所有,若您需要引用、转载,必须注明来源及原文链接即可,如涉及大面积转载,请来信告知,获取《授权协议》。
2;本网站图片,文字之类版权申明,因为网站可以由注册用户自行上传图片或文字,本网站无法鉴别所上传图片或文字的知识版权,如果侵犯,请及时通知我们,本网站将在第一时间及时删除,相关侵权责任均由相应上传用户自行承担。
内容投诉
智造资料网打造智能制造3D图纸下载,在线视频,软件下载,在线问答综合平台 » 机械工程英语——Lesson 11 Other Mechanisms(图文教程)


